Filter resources by:
Select a filter from the drop down menu to apply the filter. Page reloads upon selection

Mar 6, 2024
Metacognition and Reading Comprehension
Metacognitive practices should be a cornerstone of a language-based classroom. Explicit instruction in metacognition allows students to make deep connections between what they are reading and previously learned material. It also helps them to make sense of what they are reading and learning to determine when material does not make sense and to decide which
Read Strategy
Feb 28, 2024
Resources to Support the Writing Process: Brainstorm to Final Draft
At Landmark School, students are required to follow a five-step writing process. In order to create checks and balances as ideas evolve into written language, we approach the writing process with the following: brainstorming, organizing, composing a rough draft, proofreading, and making final edits before turning it in. Breaking a daunting task like writing an
Read Blog
Feb 27, 2024
Provide Models
Executive function researchers, such as Russell Barkley (2019), assert that the ability to picture the steps required to reach a goal is a main function of the executive functions. Further, noted executive function coach and expert Sarah Ward (2014) outlines that without a model or a clear vision of the end goal, students “are open
Read Strategy
Feb 18, 2024
Process Writing: An Overview for Teachers
The Prewriting Phase The prewriting phase is essential to helping students generate and organize their thoughts prior to writing. It establishes the roadmap of the writing piece, allowing them to see where they are going with their ideas and how they will get there. Writing without working through the steps of the prewriting phase is
Read Strategy
Feb 1, 2024
Finding the Main Idea
Scarborough’s Reading Rope, a theoretical model of reading development created by Hollis Scarborough, highlights that reading comprehension is an active process. Strong readers possess automatic word recognition skills and strategic language comprehension skills, meaning that students who read well can quickly and effortlessly read the words on the page and can also simultaneously deeply and
Read Strategy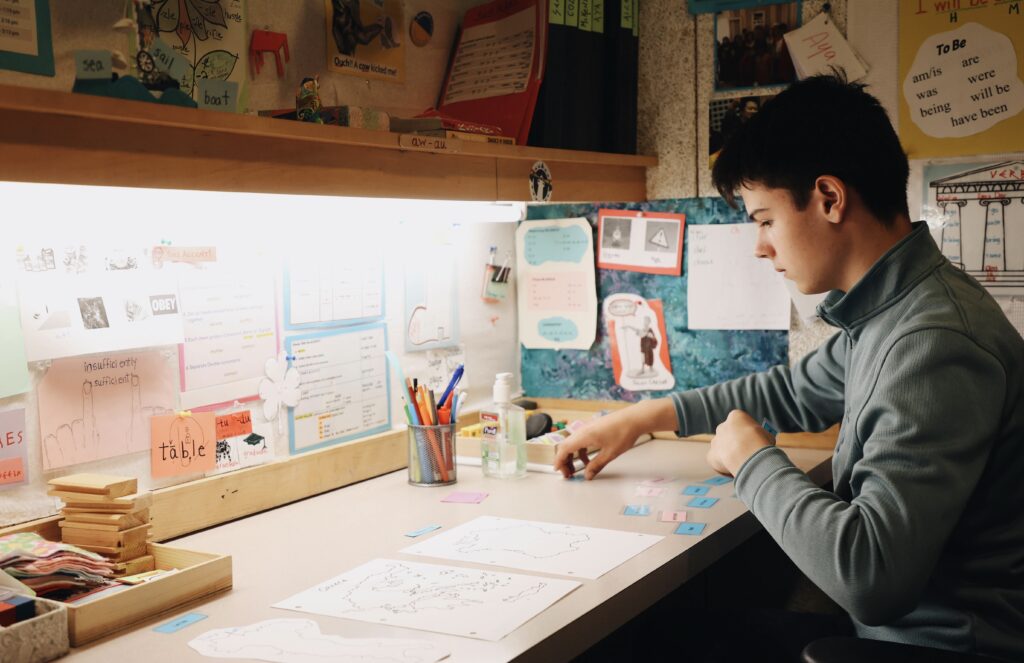
Jan 16, 2024
More Fun than Memorization: Interactive Strategies for Spelling Success
Teaching spelling can also be emotional. It can be hard for the educator to prioritize this essential activity as spell check and autocorrect become smarter, more integral supports within our primary modes of modern communication (like texting and email). Even for the teacher who has successfully integrated technology, spelling is hard because the tools available
Read Blog
Dec 8, 2023
A Morphophonemic Approach to Decoding and Vocabulary
So, why does it seem so hard? English is a deep orthography, meaning that it is a morphophonemic language, not solely a phonetic one. A phonetic language, such as Italian, has a near one-to-one correspondence between sounds and their spellings. In Italian, there are 21 graphemes (spellings) that correspond to 28 sounds. While some Italian
Read Blog
Nov 5, 2023
An AI Tsunami is Coming for Education
Like so many things, how Artificial Intelligence (AI) will transform the lives and work of educators begins with Oswald the Lucky Rabbit. It was 1928, and Ub Iwerks was in trouble. He and his partner, Walter E. Disney, had just lost the rights to their animated gold mine, Oswald the Lucky Rabbit. Following Oswald’s premier
Read Blog
Nov 1, 2023
The Executive Functions and Literacy
The graphic below provides a visual representation of the intersection of these skills. Language and literacy skills include listening, speaking, reading, and writing. Study skills include flexible and appropriate use of strategies for managing materials, time and language/information. Self-efficacy (the belief that one’s actions are related to outcomes) includes skills in self-awareness, self-assessments, and self-advocacy.
Read Strategy